Pivotal clinical trial
DUVYZAT was studied in EPIDYS, one of the most inclusive phase 3 DMD studies to date1,*
EPIDYS was a global, 18-month, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial that included patients with a broad range of genetic mutations.1,2

Ethan, an actual DUVYZAT patient for 4+ years.
Patients were:
- Ambulant boys aged ≥6 years with genetically confirmed DMD (median age of 9.8 years)1,2
- No restrictions on genetic mutations, but these were generally balanced across both groups1
- All patients completed two 4SC assessments with a mean of 8 seconds or less, were ambulatory, and had a time-to-rise of at least 3 seconds but less than 10 seconds1
- Patients were on a stable dose and regimen of corticosteroids, which was continued throughout the study1
Efficacy was assessed in 120 patients using multiple measures, including 4SC,† NSAA (including time-to-rise from the floor), 6-minute walking test, change in VLFF, knee extension and elbow flexion, and a muscle strength assessment.1
Safety was assessed in 179 patients (Group A + Group B).1
Efficacy and safety analysis group, n=120
Baseline VLFF >5% but ≤30%
Composed of patients unlikely to lose mobility suddenly but expected to show measurable decline in function, strength, and fat fraction when on placebo + corticosteroids.
Safety analysis only, n=59
Baseline VLFF ≤5% or >30%
Additional subjects recruited to assess the safety of DUVYZAT + corticosteroids in a broader population of patients with DMD.

Ethan, an actual DUVYZAT patient for 4+ years.
PROTECTION against DMD progression with DUVYZAT2
Patients treated with DUVYZAT were able to complete 4SC faster than patients taking placebo2
PRIMARY ENDPOINT: Change in time to perform 4SC vs placebo
DUVYZAT demonstrated greater preservation of motor function vs placebo as shown by NSAA1,§
SECONDARY ENDPOINT: Change from baseline in total NSAA item score over 18 months1,||
§ Nominally significant but not statistically significant based on the prespecified multiplicity adjustment.1
II The NSAA is a DMD-specific assessment scale measuring lower limb function in ambulant children with DMD, comprising 17 items scored on a scale of 0 to 2. A score of 2 indicates the activity is performed without difficulty; 1 indicates the activity is performed with some compensation; 0 indicates the activity cannot be performed independently.1,2,5
Post hoc analysis: fewer failed NSAA test items for patients on DUVYZAT vs placebo1,2
Loss of NSAA items at 18 months—target population1,2
% of patients with failure in NSAA items

Compared with placebo at 18 months,
DUVYZAT reduced new fat infiltration in key muscle groups required for ambulation1,2,7,§
SECONDARY ENDPOINT: Changes in mean VLFF over 18 months from baseline1,7
At 18 months, for the patients with VLFF baseline in the range of >5% to ≤30%, the mean increase (absolute difference from baseline levels) of VLFF was 7.48% in the DUVYZAT-treated patients compared to a 10.89% increase in patients who received placebo.2
§ Nominally significant but not statistically significant based on the prespecified multiplicity adjustment.1
Exploratory analysis: DUVYZAT reduced new fat infiltration in the thigh muscle8
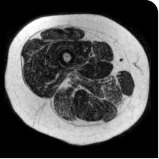
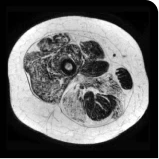
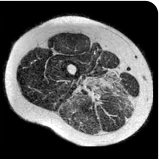
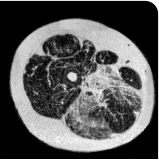
MRS imaging showing increase in fat fraction from baseline after 18 months.7
Images are from single individuals and may not be representative of all patients' results.
MRS, magnetic resonance spectroscopy.
DUVYZAT safety
DUVYZAT safety is based on the pivotal EPIDYS 18-month study in a total of 179 ambulant DMD patients aged 6 years and older on concomitant corticosteroid treatment.2 95% of patients completed the EPIDYS clinical trial.1
Adverse reactions reported in >5% of DUVYZAT-treated patients
| DUVYZAT + corticosteroids (n=118) % |
Placebo + corticosteroids (n=61) % |
|
|---|---|---|
| Diarrhea | 37 | 20 |
| Abdominal pain | 34 | 25 |
| Thrombocytopenia‡ | 33 | 0 |
| Nausea/vomiting | 32 | 18 |
| Hypertriglyceridemia | 23 | 7 |
| Pyrexia | 13 | 8 |
| Myalgia | 9 | 3 |
| Rash | 9 | 2 |
| Arthralgia | 8 | 2 |
| Fatigue | 8 | 0 |
| Constipation | 7 | 2 |
| Decreased appetite | 7 | 0 |
‡ Thrombocytopenia includes platelet count decreased and thrombocytopenia.
References: 1. Mercuri E, Vilchez JJ, Boespflug-Tanguy O, et al; EPIDYS Study Group. Safety and efficacy of givinostat in boys with Duchenne muscular dystrophy (EPIDYS): a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Neurol. 2024;23(4):393-403. 2. DUVYZAT. Prescribing information. ITF Therapeutics; 2024. 3. Muntoni F, Signorovitch J, Sajeev G, et al. Meaningful changes in motor function in Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD): a multi-center study. PLoS One. 2024;19(7):e0304984. 4. Data on file, ITF Therapeutics. 5. Ayyar Gupta V, Pitchforth JM, Domingos J, et al. Determining minimal clinically important differences in the North Star Ambulatory Assessment (NSAA) for patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy. PLoS One. 2023;18(4):e0283669. 6. Mercuri E, Brogna C, Mah JK, et al. Givinostat in DMD: results of the Epidys study with particular attention to NSAA. Poster presented at: 2023 World Muscle Society Conference; October 2023; Charleston, SC. 7. Vandenborne K. Givinostat in DMD: results of the Epidys study with particular attention to MR measures of muscle fat fraction. Oral presentation at Muscular Dystrophy Association Clinical & Scientific Conference; March 19-22, 2023; Dallas, TX.
