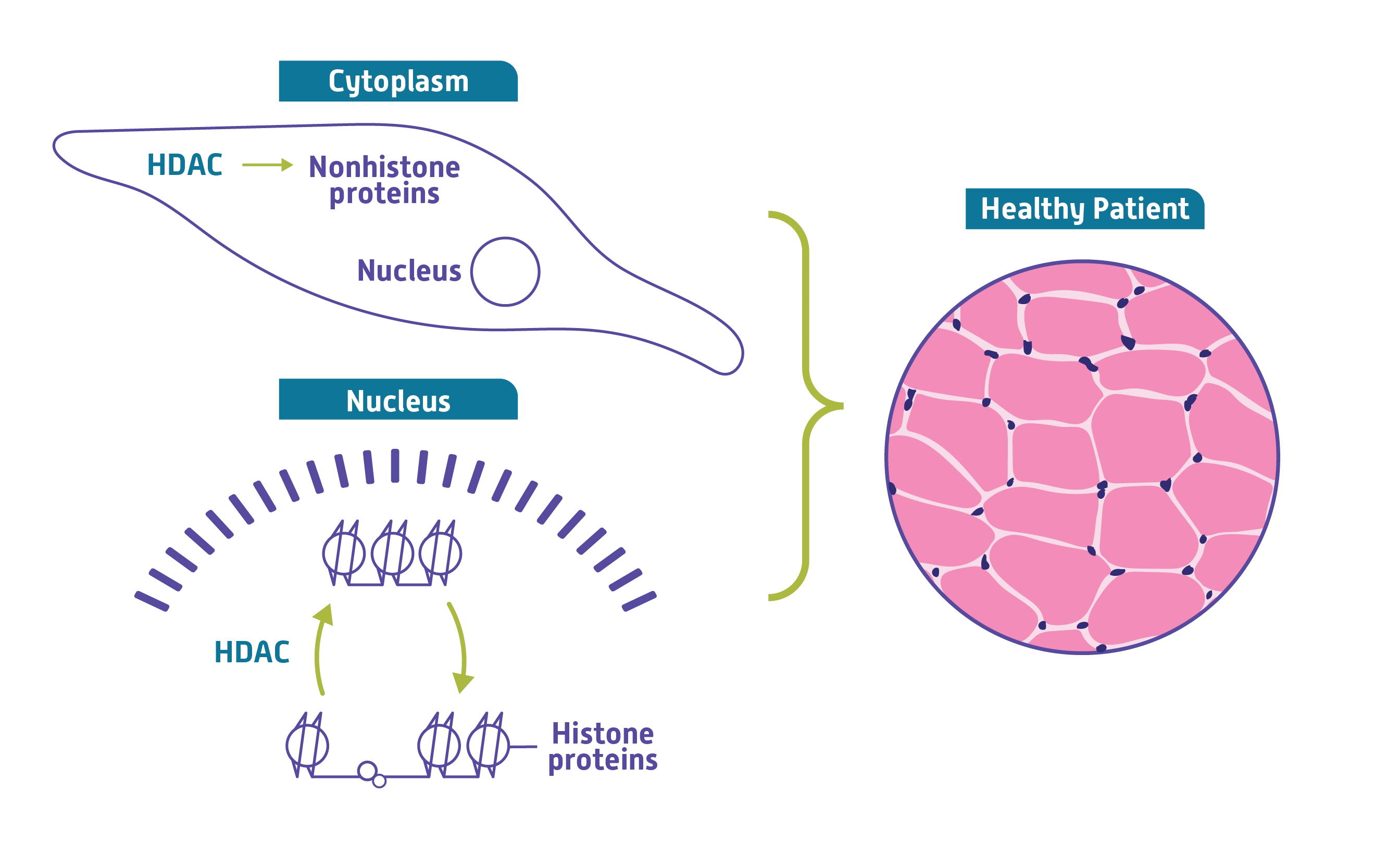
HDAC may play a key role in regulating muscle homeostasis1-6
The potential role of HDAC in normal muscle repair1-3
HDACs are thought to be important for regulating muscle homeostasis. Through nuclear and cytoplasmic enzymatic activity, HDACs modify both histone and nonhistone proteins. They may play a key role in maintaining and repairing muscle tissue by modifying proteins that regulate muscle fiber repair pathways.
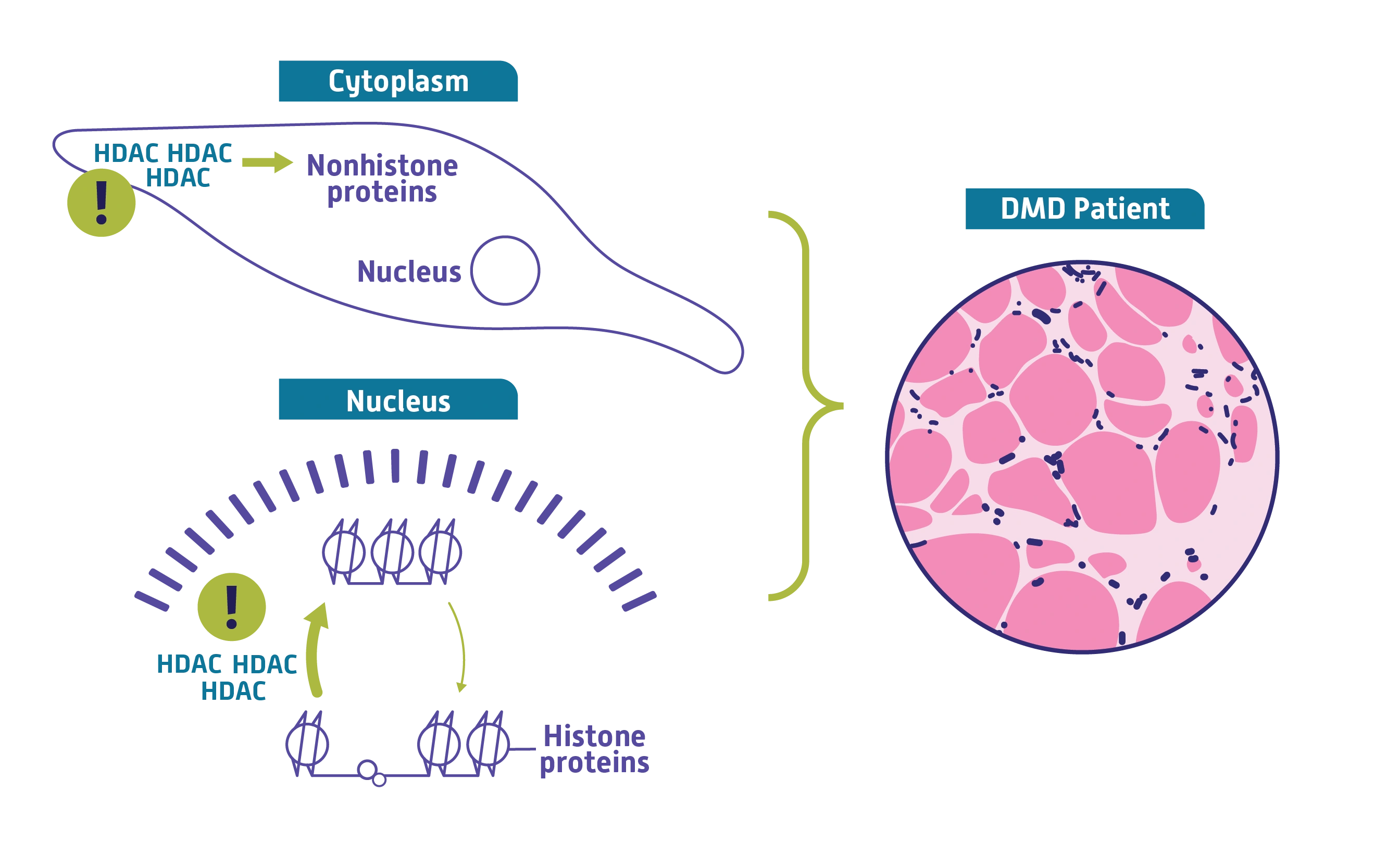
HDAC overactivity in DMD2,4,5
In DMD, HDAC is overactive.
Increased HDAC activity, in combination with the structural instability of dystrophin-deficient muscle cells, may disrupt the process of normal muscle repair and accelerate the deterioration of tissue.
HDAC upregulation may drive2,4,5:
- Activation of chronic inflammatory pathways
- Impairment of muscle repair
- Fibrogenesis and adipogenesis
- Muscular atrophy
While the exact mechanism is unknown,
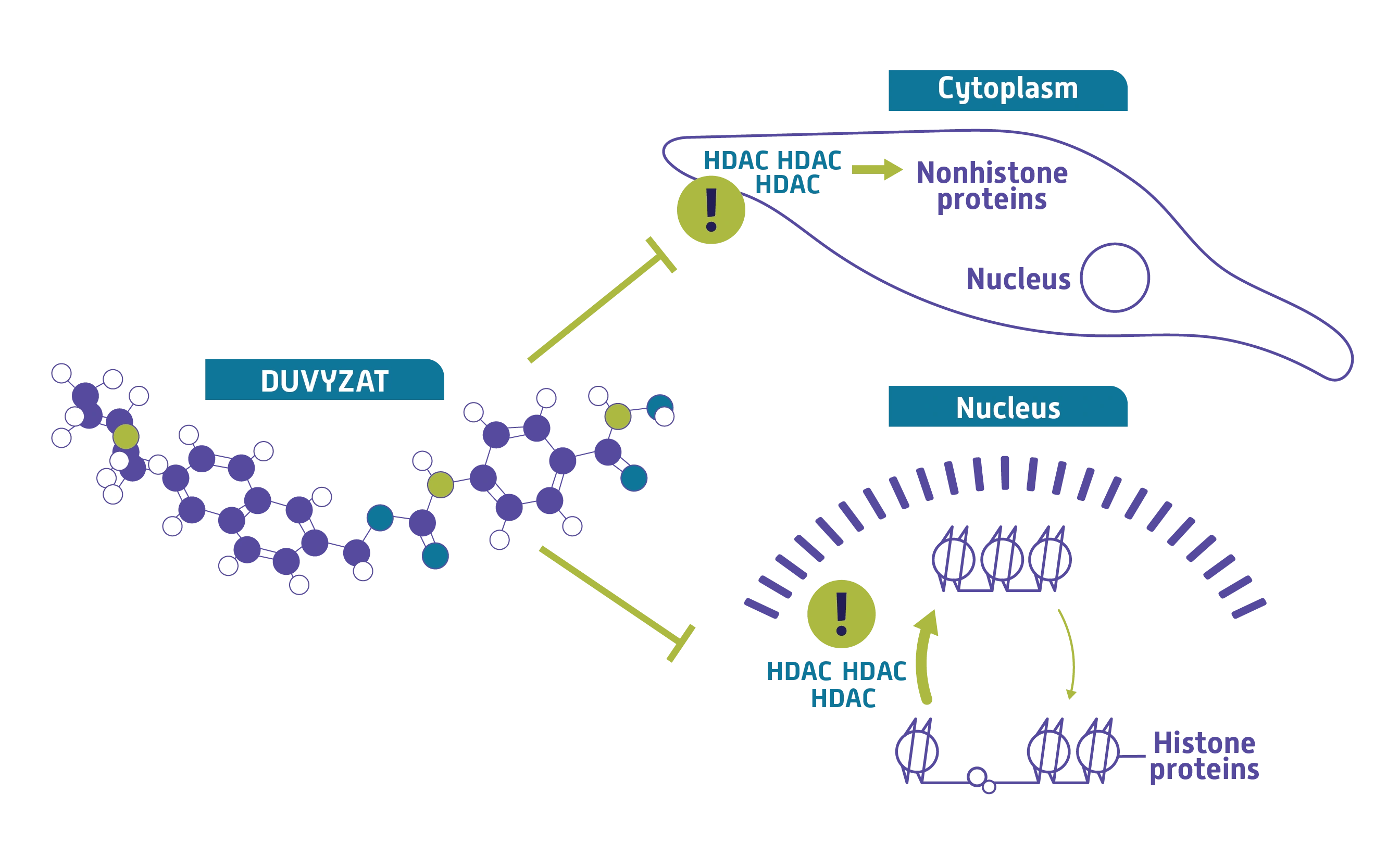
DUVYZAT targets HDAC overactivity—thought to be a key pathologic process in DMD1-6
How DUVYZAT may work5,6
DUVYZAT is a pan-HDAC inhibitor.
While its exact mechanism is unknown, DUVYZAT is designed to target HDAC, reduce its enzymatic activity, and address the key pathologic process of HDAC overactivity.
How DUVYZAT may work5,6
DUVYZAT is a pan-HDAC inhibitor.
While its exact mechanism is unknown, DUVYZAT is designed to target HDAC, reduce its enzymatic activity, and address the key pathologic process of HDAC overactivity.
References: 1. Yang C, Croteau S, Hardy P. Histone deacetylase (HDAC) 9: versatile biological functions and emerging roles in human cancer. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2021;44(5):997-1017. 2. Sandonà M, Cavioli G, Renzini A, et al. Histone deacetylases: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic implications for muscular dystrophies. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(5):4306. 3. Seto E, Yoshida M. Erasers of histone acetylation: the histone deacetylase enzymes. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2014;6(4):a018713. 4. Mercuri E, Vilchez JJ, Boespflug-Tanguy O, et al; EPIDYS Study Group. Safety and efficacy of givinostat in boys with Duchenne muscular dystrophy (EPIDYS): a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Neurol. 2024;23(4):393-403. 5. Consalvi S, Saccone V, Giordani L, Minetti G, Mozzetta C, Puri PL. Histone deacetylase inhibitors in the treatment of muscular dystrophies: epigenetic drugs for genetic diseases. Mol Med. 2011;17(5-6):457-465. 6. DUVYZAT. Prescribing information. ITF Therapeutics; 2024.
